How Do Smart Speakers Work? Have you ever wondered how your smart speaker understands your voice and responds instantly? It might seem like magic, but there’s fascinating technology working behind the scenes to make it happen.
Knowing how smart speakers work can help you use them better and even protect your privacy. You’ll discover the simple steps these devices take to listen, think, and act on your commands. Keep reading to unlock the secrets of your smart assistant and make the most out of it.
Core Components
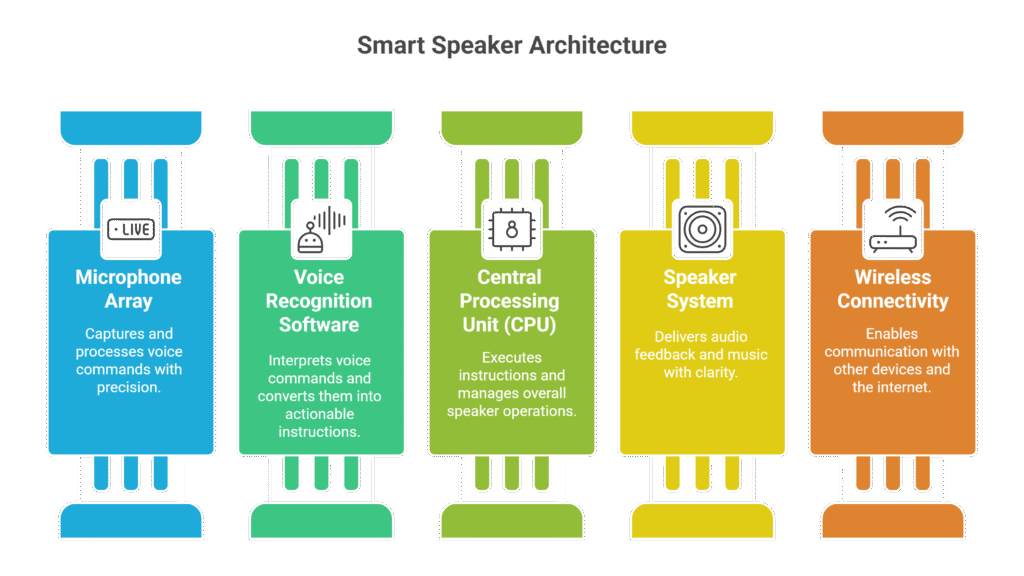
Smart speakers rely on a set of essential parts to function properly. These core components work together to listen, understand, and respond to your voice commands. Each component plays a unique role in delivering a smooth and interactive experience. Understanding these parts helps explain how do smart speakers work and why they are so effective in homes today.
Microphones And Speakers
The microphones in smart speakers are very sensitive. They pick up sounds from across the room, even when music plays loudly. Most smart speakers use multiple microphones arranged in a ring. This setup helps the device focus on your voice and ignore background noise.
- Far-field microphones: Capture your voice from a distance.
- Noise cancellation: Filters out unwanted sounds.
- Beamforming technology: Focuses on the direction of your voice.
Once the smart speaker hears your command, it uses its speakers to reply. These speakers deliver clear sound for music, alerts, and voice responses. Some smart speakers have high-quality audio drivers to provide rich bass and crisp highs. This makes listening more enjoyable.
| Component | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Microphones | Capture voice commands | Accurate voice detection |
| Speakers | Play responses and music | Clear audio output |
Many users also wonder how Bluetooth speakers work with smart TV connections. Smart speakers often support Bluetooth, allowing them to pair with TVs for better audio. This adds flexibility and enhances the home entertainment experience.
Voice Recognition Chipsets
The heart of a smart speaker is its voice recognition chipset. This small chip quickly and accurately processes your voice commands. It converts sound waves into data that the system can understand. The chipset runs advanced algorithms to recognize words and intent.
These are some key features of voice recognition chipsets:
- Noise reduction: Removes background sounds.
- Wake word detection: Listens for specific phrases like “Hey Alexa.”
- Natural language processing (NLP): Understands the meaning behind commands.
- Low power consumption: Saves battery life or energy.
The chipsets also support continuous learning. They improve over time by learning your voice patterns and preferences. This makes the smart speaker more personalized and responsive.
| Feature | Purpose | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Wake word detection | Activate the device on command | Hands-free control |
| Natural language processing | Understand user intent | More accurate responses |
| Noise reduction | Filter background noise | Clearer voice recognition |
How Do Smart Speakers Work: Connectivity Modules Explained
Connectivity modules play a crucial role in understanding how smart speakers work. These modules, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and sometimes Zigbee or Thread, connect the speaker to the internet and other devices. They enable the smart speaker to stream music, access cloud-based services, and control smart home gadgets seamlessly.
Wi-Fi is the primary connection that allows smart speakers to communicate with the cloud for quick and accurate responses. Bluetooth enables direct pairing with phones, tablets, or TVs, providing flexible connectivity. Many users often wonder how Bluetooth speakers work with smart TV setups in smart speakers. Bluetooth technology allows a wireless audio connection for enhanced sound quality without the clutter of cables.
- Wi-Fi: Connects to the internet for data and updates.
- Bluetooth: Pairs with nearby devices for audio playback.
- Zigbee/Thread: Controls smart home devices efficiently.
Smart speakers use these modules to interact with many devices. This creates a seamless smart home experience. The modules also support firmware updates to keep the speaker secure and functional.

Voice Activation
Voice activation is the heart of smart speakers. It allows these devices to respond to commands without touching buttons. Users simply speak, and the smart speaker listens and acts. This hands-free feature makes smart speakers very convenient. But how do they know when to listen? This happens through advanced voice activation technology. It involves specialized systems such as wake-word detection and continuous listening modes. These systems help smart speakers recognize when someone wants to talk to them. They keep the device ready to respond while protecting user privacy. Understanding voice activation helps us see how smart speakers work smoothly and efficiently.
Wake Word Detection
Wake word detection is the first step in voice activation. A wake word is a specific word or phrase that wakes up the smart speaker. Common wake words include “Alexa,” “Hey Google,” or “Hey Siri.” The smart speaker is always listening for this wake word, but does not record or respond until it hears it.
Here is how wake word detection works:
- Always Listening: The microphone listens constantly but only for the wake word.
- Low Power Mode: The device uses little power during this phase to save energy.
- Sound Recognition: The system compares sounds to its wake word pattern.
- Activation: Once the wake word is detected, the device fully wakes up and starts processing commands.
Wake word detection uses advanced algorithms and machine learning to reduce false alarms. The smart speaker learns to recognize the wake word even with background noise or different accents.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Wake Word | The word or phrase that triggers the device |
| Listening State | The device listens for wake word without recording |
| Recognition Technology | Machine learning algorithms identify a wake word |
| Activation | Device wakes fully and processes commands |
Continuous Listening Mode
Continuous listening mode means the smart speaker keeps listening after the wake word. It records and processes the user’s commands in real-time. This mode allows the device to understand and respond quickly. It also lets the smart speaker follow longer conversations.
Key points about continuous listening mode:
- Active Listening: The microphone captures the user’s voice until the command ends.
- Processing Commands: Voice data is sent to cloud servers for analysis.
- Privacy Controls: Users can review and delete voice recordings.
- Automatic Stop: Listening stops once the command is complete or after silence.
Continuous listening mode requires smart technology to balance responsiveness and privacy. The device listens only after hearing the wake word. This reduces the chance of recording private conversations accidentally. Many smart speakers also allow users to mute the microphone manually.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Listening Duration | From wake word until the command ends |
| Data Processing | Voice sent to cloud for command understanding |
| Privacy Options | User control over voice data and the microphone |
| Automatic Stop | Stops listening after silence or command completion |
Speech Processing
To truly understand how do smart speakers work, it’s important to look at speech processing, the core technology that powers their intelligence. Speech processing allows these devices to listen, interpret, and respond to your voice commands accurately.
When you speak to a smart speaker, it captures your voice input and converts the sound waves into digital data. This data then moves through several stages where the system analyzes what was said and determines the appropriate response.
The process involves capturing speech, recognizing words, understanding meaning, and generating a reply. To handle these tasks efficiently, smart speakers use a combination of local and cloud-based processing, ensuring fast responses and natural, human-like interactions.
Local Vs Cloud Processing
Smart speakers rely on two main types of speech processing: local processing and cloud processing. Each has unique advantages and limitations.
- Local Processing: Happens inside the device itself without sending data to external servers.
- Cloud Processing: Sends speech data to powerful remote servers for analysis.
Local processing is faster because it does not depend on internet speed. It handles simple commands like turning on lights or setting alarms. Privacy is better since your voice data stays on the device. However, local processing has limited power and storage. It cannot handle complex tasks or understand natural language deeply.
Cloud processing uses advanced servers with more computing power. It can analyze complex commands, access updated information, and improve over time through machine learning. The cloud helps smart speakers understand different languages and accents better. The downside is that it requires an internet connection, which can cause delays. Privacy concerns also arise because your voice data leaves your home.
| Feature | Local Processing | Cloud Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast response | Depends on the internet |
| Privacy | High (data stays local) | Lower (data sent online) |
| Complexity | Simple tasks | Complex tasks and learning |
| Dependence | No internet needed | Requires internet |
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the technology that helps smart speakers understand human speech naturally. It breaks down voice data into parts to find meaning. NLP allows the device to recognize words, grammar, and context.
Here are the key steps NLP uses:
- Speech Recognition: Converts sound into text.
- Syntax Analysis: Examines sentence structure to identify grammar.
- Semantic Analysis: Understands the meaning behind words.
- Intent Detection: Finds out what the user wants to do.
- Response Generation: Creates a reply or action based on intent.
NLP improves smart speakers by allowing more natural conversations. It helps the device handle different accents, slang, and sentence styles. The technology learns from each interaction to get better over time.
Examples of NLP in smart speakers:
- Answering questions like “What’s the weather today?”
- Understanding commands like “Play my favorite song.”
- Managing tasks such as “Remind me to call mom.”
- Holding simple conversations for a better user experience.

Command Execution
To understand how do smart speakers work, it helps to explore the process of command execution—the stage where your voice commands turn into real actions. After you speak, the smart speaker quickly interprets your words, determines your intent, and performs the required task.
These actions can include controlling smart home devices, playing music, providing information, or even interacting with other apps and services. Command execution is what brings voice control to life, making smart speakers practical and powerful tools for everyday use.
Device Control
One of the main uses of smart speakers is to control other devices around the home. When you give a command like “turn on the lights” or “set the thermostat to 72 degrees,” the speaker sends a signal to those devices. This happens through wireless connections such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee.
Common device control commands include:
- Turning lights on or off
- Adjusting thermostat settings
- Locking or unlocking smart locks
- Controlling smart plugs and appliances
- Playing music or changing volume on smart TVs
Smart speakers act as a central hub for your smart home. They understand your voice commands, translate them into digital instructions, and send those instructions to the right device. This process is usually fast, taking less than a second.
| Device | Connection Type | Example Command |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Lights | Wi-Fi, Zigbee | “Turn off living room lights.” |
| Thermostat | Wi-Fi | “Set the temperature to 70 degrees.” |
| Smart Lock | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi | “Lock the front door.” |
Information Retrieval
Smart speakers access vast amounts of data to answer your questions or provide information. When you ask, “What’s the weather today?” or “Who won the game last night?”, the speaker connects to the internet and searches online databases. It then reads the answer aloud.
This process includes several steps:
- Voice recognition to capture your question
- Sending the query to cloud servers
- Searching trusted sources like weather services or news sites
- Returning a simple, spoken answer
Information retrieval covers many types of requests:
- Weather updates
- News headlines
- Sports scores
- General knowledge questions
- Conversions and calculations
The smart speaker simplifies complex data into easy-to-understand responses. It removes the need for users to read or search on their own. This makes it helpful for quick answers while cooking, driving, or doing other tasks.
Third-party Integrations
Smart speakers connect with many apps and services beyond their own built-in features. These connections are called third-party integrations. They allow the speaker to perform extra functions by working with other companies’ software or devices.
Examples include:
- Ordering groceries from online stores
- Booking a ride with ride-sharing apps
- Controlling smart home devices from different brands
- Playing music from streaming services
- Managing calendars and to-do lists
Third-party integrations require permissions. You usually link your accounts in the smart speaker’s app. This connection lets the speaker send commands to external services securely.
Integration flow example:
User says: “Order milk from grocery app” ↓ Smart speaker sends request to cloud ↓ Cloud forwards request to grocery service API ↓ Order placed and confirmation sent back to speaker ↓ Speaker announces: “Your milk will arrive tomorrow”These integrations make smart speakers more powerful. They expand the range of tasks your device can handle, making everyday life smoother and more connected.

Privacy And Security
Smart speakers have become common in many homes, but many users still wonder how do smart speakers work? These intelligent devices use voice recognition technology and AI assistants to listen, respond, and assist with everyday tasks through natural language processing. Understanding how smart speakers work also involves exploring how they use machine learning to improve accuracy, connect to the cloud, and integrate seamlessly with other smart home devices for real-time responses and automation.
However, this advanced connectivity raises important questions about privacy and data security. Users want to know how their voice data is stored, processed, and protected from unauthorized access. By exploring how smart speakers work, people can better understand the balance between convenience and security, helping them make informed decisions for a safer and more trusted smart home ecosystem.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a key method for protecting information sent between smart speakers and servers. It changes data into a secret code that only authorized devices can read. This stops hackers from stealing or reading private conversations.
Encryption happens at different stages:
- Voice Capture: When you speak, your voice is converted into digital data.
- Data Transmission: This data is encrypted before leaving the device.
- Cloud Storage: Your data stays encrypted while stored on remote servers.
Here is a simple comparison of data states:
| Data State | Description | Encryption Status |
|---|---|---|
| At Rest | Data stored in the device or cloud | Encrypted to prevent unauthorized access |
| In Transit | Data moving between devices and servers | Encrypted with secure protocols like TLS |
| In Use | Data is being processed by the smart speaker | Temporarily decrypted but isolated in secure environments |
Strong encryption standards such as AES-256 and TLS protect your data. These standards are widely used and trusted globally. They make it almost impossible for outsiders to understand the data without the right keys.
Without encryption, voice commands and personal details would be at risk. Encryption ensures that only the smart speaker and its trusted services can access your information.
User Consent And Controls
User consent is crucial for privacy with smart speakers. These devices only start recording after hearing a specific wake word. This design reduces unwanted listening. Users must also agree to the device’s terms before use.
Many smart speakers offer settings that let users control their data. These controls include:
- Turning off the microphone physically or via software
- Reviewing and deleting voice recordings
- Managing data sharing preferences
- Setting privacy alerts and notifications
Here is a list of common user controls:
- Microphone mute button: Stops the device from listening temporarily.
- Voice history management: View or delete past voice commands.
- Privacy dashboard: Central place to adjust data sharing and permissions.
- Notification settings: Alerts for data use or privacy changes.
Smart speaker companies also update privacy policies regularly. Users get informed about how their data is used. Transparency builds confidence and helps users make smart choices.
Active user control means you decide what the device can do. It keeps your information safe and respects your privacy preferences. Always check your device’s settings to stay in control.
Evolution And Future Trends
Smart speakers have evolved significantly since their first introduction. These devices started as simple voice-activated assistants and now play a vital role in many homes. The evolution continues as technology improves and new features are added. Understanding the future trends helps us see how smart speakers will become even more useful and intelligent.
Improved Ai Capabilities
The heart of any smart speaker is its artificial intelligence (AI). Over the years, AI has become smarter and faster at understanding user commands. Early smart speakers could follow only simple instructions. Now, they can handle complex questions and multitask.
Key improvements include:
- Better speech recognition, including accents and noisy environments
- Context awareness, allowing follow-up questions without repeating details
- Natural language processing that feels more like a real conversation
- Learning user preferences to personalize responses
The table below compares AI features in early vs. modern smart speakers:
| Feature | Early Smart Speakers | Modern Smart Speakers |
|---|---|---|
| Speech Recognition | Basic commands only | Understands accents and noisy rooms |
| Context Awareness | Limited | Follows multi-step conversations |
| Personalization | None | Adapts to user preferences |
AI improvements mean smart speakers will soon predict needs and proactively offer help. This change makes interactions smoother and more natural.
Enhanced Connectivity
Connectivity is crucial for smart speakers to access information and control other devices. Early models used Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Now, connectivity options are expanding rapidly.
New connectivity features include:
- Support for faster Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6
- Integration with smart home protocols like Zigbee and Z-Wave
- Better Bluetooth versions for improved device pairing
- Cloud-based syncing for seamless user experience across devices
Enhanced connectivity allows smart speakers to work well with a wide range of smart devices. This creates a more connected home environment.
Below is a brief overview of connectivity improvements:
| Connectivity Type | Early Speakers | Modern Speakers |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) |
| Smart Home Protocols | Limited or None | Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 4.0 | Bluetooth 5.2 |
Improved connectivity increases reliability and speed. It also allows smart speakers to act as hubs for smart homes.
New Use Cases
Smart speakers were once only for playing music or answering questions. Today, they have many new uses that impact daily life.
Emerging use cases include:
- Home automation: Control lights, thermostats, and security systems with voice.
- Health monitoring: Track fitness, remind about medications, or guide meditation.
- Education: Help children learn languages or facts through interactive lessons.
- Work assistance: Schedule meetings, set reminders, or transcribe notes.
- Entertainment: Play games, tell stories, or provide interactive experiences.
These new uses make smart speakers valuable for people of all ages and needs. The technology will keep expanding into areas like:
- Personalized wellness coaching
- Smart kitchen appliances control
- Voice-activated shopping and payments
- Enhanced accessibility for people with disabilities
Smart speakers are becoming central to a smart lifestyle. Their role will grow as developers find new ways to use voice technology.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Smart Speakers Work to Recognize Voice Commands?
Smart speakers use built-in microphones to capture your voice. They process commands using speech recognition technology. This technology converts speech to text. Then, the device matches commands with pre-programmed actions or online services to respond accurately.
What Technology Powers Smart Speakers’ Voice Control?
Smart speakers rely on natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies understand and interpret spoken language. They enable the device to respond contextually and improve over time through machine learning.
How Do Smart Speakers Connect To The Internet?
Smart speakers connect via Wi-Fi networks. This connection allows them to access cloud services and online databases. The internet link is essential for streaming music, answering questions, and controlling smart home devices.
Are Smart Speakers Always Listening To Conversations?
Smart speakers listen for a wake word but don’t record continuously. They only start processing audio after detecting this trigger. Privacy settings let users control data storage and manage voice recordings.
Conclusion
How Do Smart Speakers Work? They listen to your voice and respond in real time using internet connectivity and cloud-based services to deliver accurate results. These devices learn from your commands over time, making interactions more personalized and helpful.
From playing music to setting reminders, smart speakers use advanced but user-friendly technology to simplify daily tasks. Understanding how they work helps you get the most out of them. They bring convenience, efficiency, and a touch of intelligence to your home—try one and see how well it fits your lifestyle.





